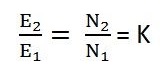EMF Equation of Transformer and Voltage Turn Ratio
Consider an AC voltage of magnitude “V” having frequency “f” is applied to the primary side of the transformer. ac flux Φm is set up in the transformer core, this flux links with the both primary and secondary winding of the transformer. the value of induced emf can be calculated using EMF equation of the transformer, also we will derive the voltage and turn ratio of the transformer.
EMF Equation Of Transformer
The derivation of the EMF Equation of the transformer is shown below.
Let
- Φm= Maximum value of flux in the core, Wb
- f= Frequency of a.c input supply in Hz
- N1 = number of turns in the primary winding
- N2 = number of turns in the secondary winding
- Φ= the flux per turn in Weber
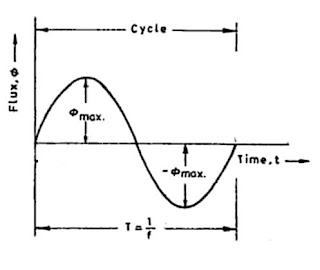
Since flux increases from its Zero value to the maximum value Φm in one-quarter of the cycle
the sinusoidal flux Φ produced by the primary winding can be expressed as
Φ=ΦmSinωt
The instantaneous emf induced in the primary is given as,
e= -N1 dΦ/dt
= -N1 d/dt (ΦmSinωt)
= –ω N1 Φm Cosωt
= -2πf N1 ΦmCosωt
= 2πf N1 Φm Sin(ωt-90)
from the above equation of emf, it is clear that the maximum value of induced e.m.f in the primary is
Em1=2πf N1 Φm
The r.m.s value primary emf is
E1=Em1/√2
= 2πf N1 Φm/√2
E1=4.44 f N1 Φm
Similarly, rms value of secondary emf is
E2=4.44 f N2 Φm
The above formula represents the emf equation of the transformer
For ideal transformer E1=V1 and E2=V2
Voltage and Turn Ratio of Transformer :
The ratio of E/N is called Voltage Per Turn of the transformer
Primary voltage per turn equation
E1/N1=4.44 f Φm
Secondary voltage per turn equation
E2/N2=4.44 f Φm
From the above equation, we can see that the voltage per turn of a transformer in both windings is the same.
The above equation is called a turn ratio of the transformer and K is called the transformation ratio.
Voltage Transformation Ratio(K): The transformation ratio is defined as the ratio of the secondary voltage to primary voltage and is denoted by K.
- If N2>N1 then the transformer is called a step-up transformer
- If N2<N1 then transformer called to step down transformer